What is VancoPK®?
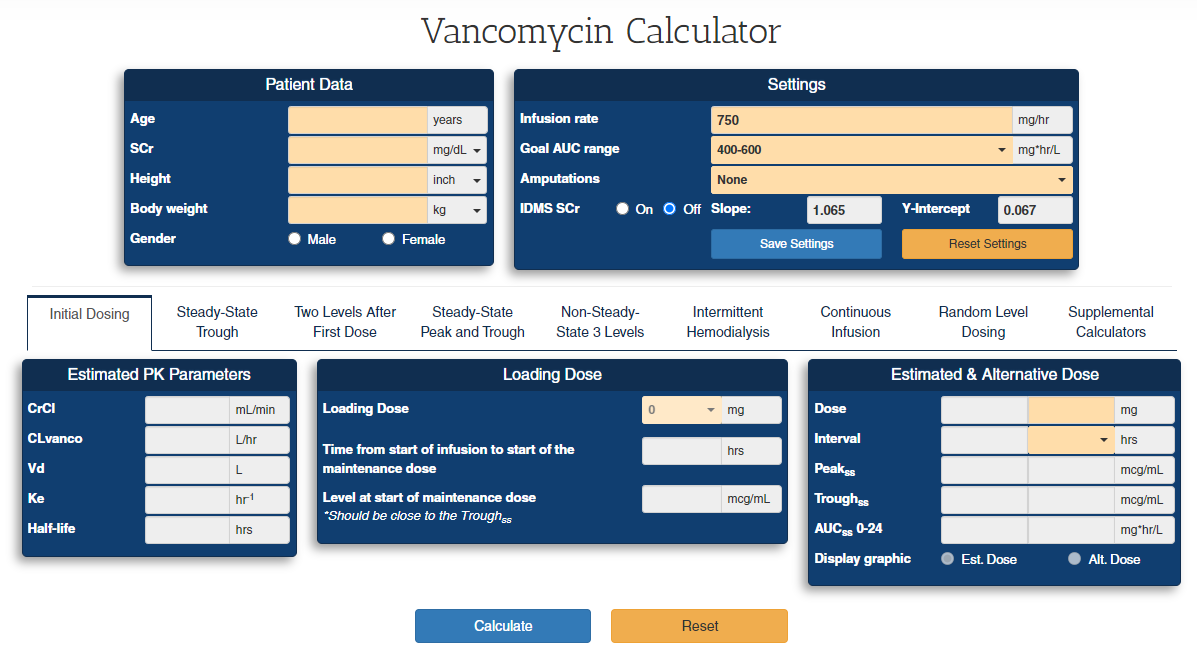
Initial Dosing Calculator: The maintenance dose is calculated based on CrCl. Clinical judgment can be used to adjust SCr and CrCl if needed. Use the loading dose calculator to achieve therapeutic levels quickly and make the first trough closer to full steady state. Note that the calculator increases Vd by 25% for the loading dose because Vd is larger at the start of therapy.
Two Levels After First Dose Calculator: This calculator may be useful for bed bound patients, when the Cockcroft-Gault equation may not be reliable to estimate CrCl.
Steady-State Trough Calculator: The trough does not have to be a trough, it can be drawn any time after distribution has finished (at least 60 minutes after the end of infusion). This calculator uses a population Vd model in first-order PK equations estimate the AUC. The correlation between peak-trough AUCs and trough-only estimated AUCs is about 0.926. The standard deviation of the difference between peak-trough and estimated AUCs is about 50, meaning that approximately 95% of patients have an estimated AUC within 100 points of the actual AUC. See the publications below for details:
- Fewel N. Vancomycin area under the curves estimated with pharmacokinetic equations using trough-only data. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021
- Fewel N. Accuracy of vancomycin AUC values estimated with trough-only data in a veteran population. AJHP. 2023
- Arensman Hannan KN, Rivera CG, Fewel N. Vancomycin AUC values estimated with trough-only data: Accuracy in an adult academic medical center population. AJHP. 2023
- Keil E, Wrenn RH, Deri CR, et al. Comparison of open-access, trough-only online calculators versus trapezoidal method for calculation of vancomycin AUC. Ann Pharmacother. 2023
Steady-State Peak and Trough Calculator: Although reliable, this method requires obtaining an additional blood sample and the results can be difficult to interpret. To help evaluate the results, compare the peak-trough AUC to the AUC estimated with the Steady State Trough calculator. If the difference between the AUCs is >100 points there may be a problem with how the peak and trough levels were drawn, reported, or entered into the calculator.
Intermittent Hemodialysis Calculator: The key to this calculator is to target a pre-dialysis level of about 20 mcg/ml because this will give a daily AUC of about 500. Enter a pre-dialysis level into the calculator to estimate a post-dialysis dose.
Continuous Infusion Calculator: This dosing method is the easiest way to measure an AUC: AUC24 = SS level * 24 hrs. The calculator has a feature where it suggests a bolus dose or hold time when a measured level is below or above the goal SS level.
Dosing by Random Levels Calculator: This calculator uses a population Vd to calculate Ke based on a random level. The results are limited to calculating a one-time dose rather than a maintenance dose.